

Low latency is one of 5G’s most important features. Combined with beamforming, small cells can deliver extremely fast coverage with low latency. Using small cells, the deployment of 5G with millimetre wave based carriers can improve overall coverage area. Testing of 5G range in mmWave has produced results approximately 500 meters from the tower.
#4g lte mbps code#
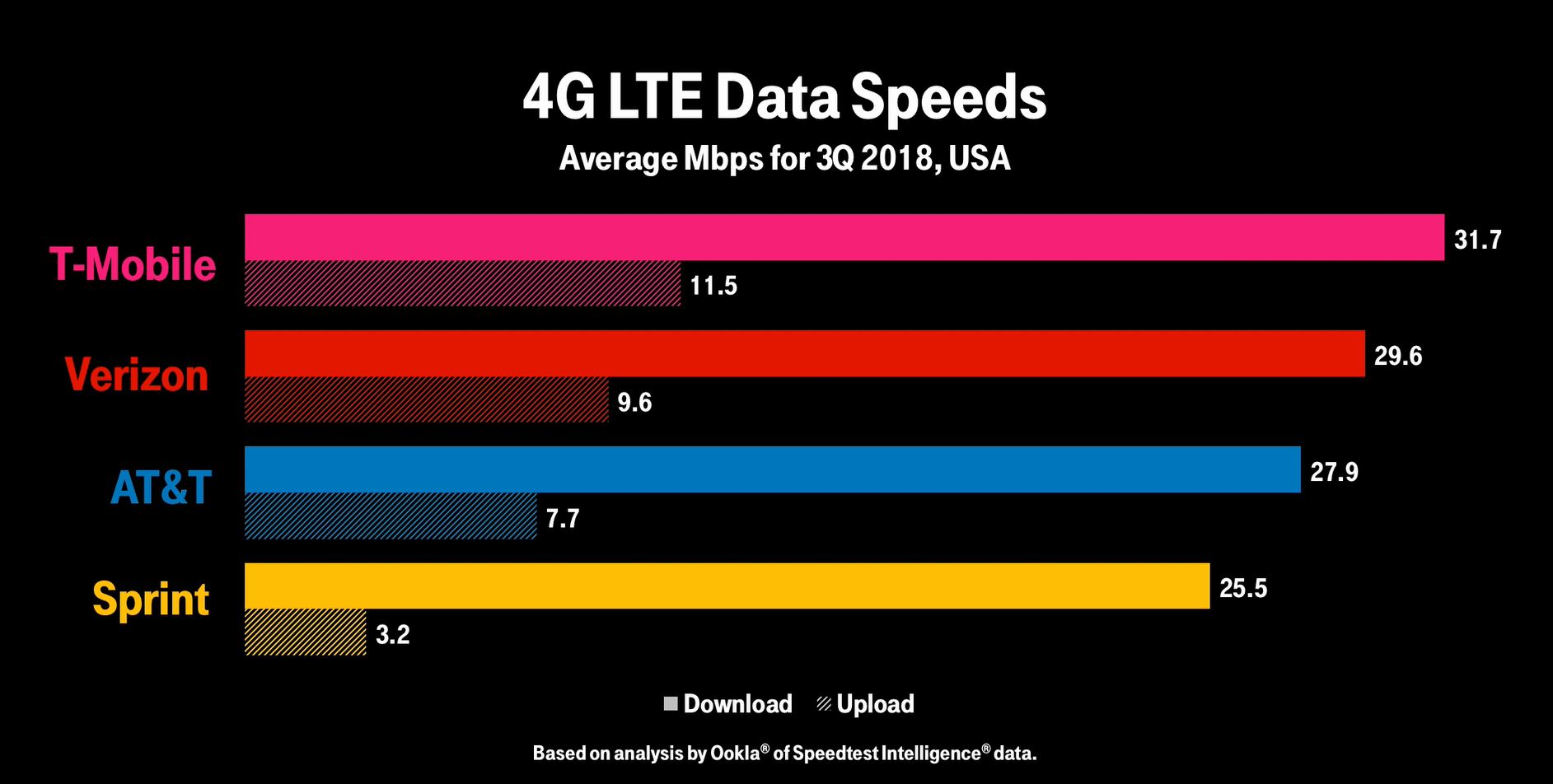
Mobile network code for Vodafone as shown in the image below:ĥG networks operate on rarely used radio millimeter bands in the 30 GHz to 300 GHz range. The result displays 4G and 5G data points with peak throughput in a particular location for ‘23415’ mobile network operator i.e. We conducted a comparison test campaign of 4G and 5G with our RantCell app. Live 5G vs 4G speed test performed via RantCell App High speed, high capacity and low cost per bit (Speeds of up to 20 Mbps or more.)įollowing is the comparison between 4G and 5G speeds: Support interactive multimedia, voice, video. 4G LTE is the term given to the path which has to be followed to achieve those predefined standards. Basically, 4G is the predetermined standard for mobile network connections. 4G LTE is a “fourth generation long term evolution”, capable of delivering a very fast and secure internet connection. What is the difference between 4G and LTE?Įven after it was widely available, many networks were not up to the required speed of 4G. While 4G LTE is a major improvement over 3G speeds, it is technically not 4G. The most important 4G standards are WiMAX and LTE. The key technologies that have made 4G possible are MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) and OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing). There is also a huge difference between 3G and 4G technology. The main difference between 3G and 4G is the data rate. International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) were the specifications by the International Telecommunication Union for the 3G network theoretically, 21.6 Mbps is the max speed of HSPA+.
Large capacities and broadband capabilities Increased bandwidth and data transfer rates It operates at a range of 2100 MHz and has a bandwidth of 15-20 MHz. It used Wide Band Wireless Network that increased clarity. By using packet switching, the original technology was improved to allow speeds up to 14 Mbps. 3G network combines aspects of the 2G network with new technologies and protocols to deliver a significantly faster data rate. The 3G standard utilises Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) as its core network architecture. Some of the key features of 2G were:Įnabled services such as SMS and MMS (Multimedia Message) During 2G, cellular phones were used for data along with voice. 2G capabilities were achieved by allowing multiple users on a single channel via multiplexing. The radio signals used by the 1G network were analog, while 2G networks were digital. Some of the country's first 5G handsets lack mmWave support and can only take advantage of mid-band 5G signals.2G refers to the second generation of mobile networks based on GSM. While delivering fast speeds and high capacity, this spectrum has very limited coverage compared with the 3.4-3.8 GHz "mid-band" spectrum typically used for 5G in most of the other countries including Australia.Īustralian 5G operators are not expected to gain access to 26GHz mmWave spectrum for several years, with the ACMA due to begin allocating 26GHz spectrum in the second half of 2020. The USA's impressive lead is due to the fact that network operators there have access to 26GHz "millimetre wave" spectrum for 5G.
#4g lte mbps download#
The USA tops the 5G real-world maximum download leaderboard at 1815 Mbps, well ahead of Switzerland on 1145 Mbps and South Korea on 1071 Mbps. We expect the 5G maximum speed seen in Australia to improve over time similarly." "In South Korea, the maximum speed we’d seen when we wrote the recent 5G Insight on Korea was 988 Mbps, but we’ve now seen a test at 1071 Mbps. "This is most likely due to the quality of the 4G experience in Australia and the large 4G spectrum holdings held by some operators. "What we have seen in Australia is one 4G speed test in the real world that is much, much closer to the 4G theoretical maximum speed than we have seen in the other countries," says Opensignal vice president of analysis Ian Fogg.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
